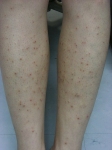
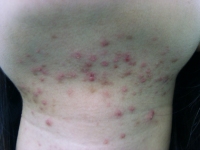
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles usually caused by an infection with bacteria, although it can be due to chemical irritation (e.g. after-shaves) or by physical irritation (e.g. shaving, waxing). Typical body sites that are involved in folliculitis include the face, scalp and legs.
Folliculitis can affect anyone, at any age, but is more common in people who have diabetes mellitus or have compromised immune systems.
Other factors that may contribute to folliculitis include chronic skin diseases such as atopic eczema, tight occlusive clothing, sweating with hot and humid environment, and carriage of staphlococcus in the nasal passages.
Signs
Superficial folliculitis appears as a red and swollen pimple, with or without pus seen, either as a single one or in a cluster of multiples, around hair follicles. Pus-filled blisters may break open and crust over. It is painful and itchy.
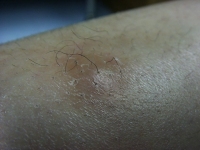
Deep folliculitis starts deeper and affects the entire hair follicle. It appears as a large swollen bump and usually filled with pus. It can cause scarring, keloid formation and hair loss.
|
|
|
The regional lymph nodes may be enlarged and become painful.
Management & Treatments
Superficial folliculitis often clears by itself in a few days, but deep or recurring folliculitis may need medical treatment. Topical antiseptics such as triclosan, clorhexidine or povidone-iodine may be used to treat and prevent superficial folliculitis
For deeper folliculitis, topical or oral antibiotics are usually required. Steps are also needed to prevent damages and irritations such as avoid shaving in the affected area. If shaving is necessary, use a clean new razor blade each time. Washing the skin with an antibacterial soap may keep down the recurences.