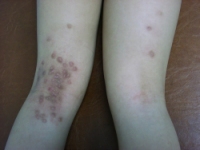
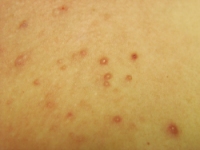
It is an infection of the skin by a poxvirus. It is common in children and spreads by direct body contact among schoolmates or siblings. It can occur anywhere on the body, but is frequently seen on the face, limbs, and hands.
Sometimes it is spread through contact with contaminated objects such as towels, or toys. It can also spread through sexual contact where the lesions happen in the genitalia.
Signs
It appears as a small, pearl colour, dome-shaped lump, filled with some fluid. It often has a dimple in the centre, with a central plug of white, cheesy material. They may occur in lines when the patient has scratched the lesion and spread the infection along the scratch line. Very often they appear as a corp.
|
|
|
The typical size is about 2 - 5 mm in diameter. There is usually no inflammation unless it has been scratched or irritated.
Management & Treatments
For people with normal immunity, they often disappear on their own after a few months to 2 years. Therefore no treatment may be required, but during this period topical treatment such as calamine lotion may be used to reduce the itch and prevent spread through scratching. Close body contact should be avoided to minimise spread to other people.
If necessary the lesions can be treated individually by cryotherapy, cautery or CO2 laser.