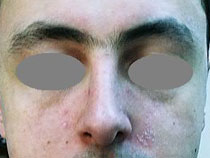
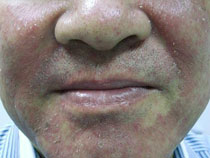
Seborrhoeic eczema has nothing to do with sebum, the oily secretion on the skin, and so the name is not appropriate. It affects all age groups from young adults to the elderly. A type of seborrhoeic eczema is also seen in babies during the first year of life, and has been described earlier.
Skin infection by yeast called Pityrosporum Ovale is thought to play a part. It is a commensal organism present on the skin of almost everyone. Normally it does not cause any symptoms, and only when someone turns allergic or sensitive to its presence, then problems arise.
There is some correlation between this and a nervous or anxious life style and personality.
Signs
The most common places are the scalp, eyebrows, centre of eyebrows, sides of nose, and cheeks. Less commonly, it affects the centre of chest and back. Occasionally it is present in skin folds such as the groins and under the breasts.
On the scalp and face, the skin is greasy, red and scaly. The condition varies in severity. A mild case would be a little bit of dandruff and flaky skin over the face. In severe cases, the skin is widely affected and very itchy; the scalp is itchy, oily and, if very inflamed, there is much scaling of the scalp skin.
|
|
|
On the chest, there is a red scaly patch over the breastbone; while on the back, there are multiple red raised dots across and between the shoulder blades. Because of the trapped moisture, there is seldom any scale in the skin folds, rather a moist red skin is seen in the groins, under the breasts and in the armpits.
Management & Treatments
A lot of people rely on steroid cream to control the itchiness and flakiness. This only suppresses the allergic component, while leaving the Pityrosporum Ovale unaffected, and could even increase. Therefore the situation can get much worse once the steroid cream is stopped, with rebound redness affecting the whole face, and more difficult to treat.
A correct regime is to use mild steroid (1% hydrocortisone) only, with added anti-fungal cream such as Miconazole, Clotrimazole, which will reduce the number of Pityrosporum Ovale.
As Pityrosporum Ovale is a normal commensal, it is not possible to eradicate them all. The aim is to control the eczema with the least frequent application of cream, as in using anti-dandruff shampoo twice a week to control dandruff.
Medicated shampoos containing anti-yeast medication may keep mild activity under control. The preparations include tar, selenium sulphide, and ketoconazole. If there is a lot of scaling, additional treatments with some steroid solutions can be needed.