What Is Laser?
Laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
In the molecular level, all physical matters have molecules that are surrounded by multiple orbits of electrons. The electrons in the outer orbits carry higher energy levels, but are also more unstable. When a molecule is Stimulated by an external energy, the electrons will absorb this energy and “jump” to higher energy orbits and “store up” this energy.
Since they are unstable in the higher orbits, they will return to the lower orbits after a while, releasing the energy again. In some materials, the released energy in such a process forms a Radiation and is Emitted out. When this process is Amplified to involve hundreds of millions of molecules, and their electrons release the energy simultaneously, this forms a LASER.
Principles Of Laser Treatments
Some materials can be used as mediums to produce lasers by stimulation. These include ruby, dyes, neodymium, alexandrite, carbon dioxide gas, and many others. Different mediums will produce lasers of different wavelengths.
When a laser hits on a target, it may be absorbed and the interaction will produce heat energy, destroying or changing that target’s nature. Each target has a different absorption spectrum of wavelengths, i.e. it absorbs different wavelengths to different degrees. So in order to hit a target strong enough, a laser that is preferentially absorbed by that target should be selected.
We call these targets chromophores. The main chromophores in the skin are water, melanin pigment, cells of blood vessels, and oxygenated blood pigment. They are located in different skin levels, and also have different absorptions to different wavelengths.
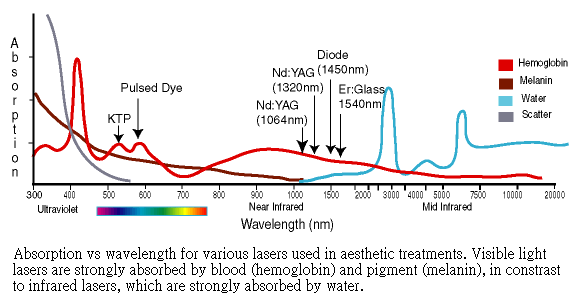
When we use lasers with different wavelengths and energy intensities, we can penetrate into different levels, selectively damage different targets. We call this selective photo-thermolysis.
When melanin is hit, for example in the case of freckles, it is shattered into tiny particles, which are then small enough to be removed by cells called macrophages.
The melanin in the hair root is there to attract the laser, and when it is hit, the heat generated will destroy the root so that further hair growth is slowed down.
Similarly, the oxygenated haemoglobin inside the blood vessels is used to attract the laser, and when it is hit, the heat generated will destroy the blood vessels, interrupt the blood flow, and remove the unattractive red and blue lines, and vascular birthmarks.
Types of Lasers
There are many ways to categorise different lasers, and there is not a fixed or good system. For aesthetic skin lasers, the first broad division is separate them into ablative and non-ablative lasers. Ablative lasers target the water content in the skin and work by vaporising the top layers of the skin to remove blemishes, scars and wrinkles, and let the skin to heal and regenerate. Non-ablative lasers penetrate and work beneath the top layers of the skin without vaporising them.
Then we can classify them according to the mediums that are used to produce the laser, the wavelenghts of lasers produced, the sources of stimulation, the chromophores being targeted, and the applications.
Recently a new technology has been developed, where the laser is emitted by a scanner in a fractionated manner of numerous small beams. So a new category of non-fractional and fractional lasers is created.
- Ablative or non-ablative lasers
- Mediums (gas; chemicals; dyes; solid-state; metal vapour)
- Wavelengths
- Stimulation sources (electrical discharge; flashlamp)
- Chromphores (water; melanin; haemoglobin)
- Applications (pigment; tattoo; vascular; skin tightening)
- Conventional or fractional
Mixing these categorisation, we arrive at a simple but useful classification for the common lasers used in skin aesthetic treatments:
Ablative Lasers
- CO2 Laser (gas medium laser,10600 nm)
- Conventional
- Fractional
- Erbium-YAG Laser (solid-state laser, 2940 nm)
- Conventional
- Fractional
As mentioned, they target the water content in the skin, and the penetration is shallow. CO2 laser can make the skin contract, seal small blood vessels and so has a blood clotting property, which is very useful. Erbium-YAG laser vaporises an even thinner layer, but the drawback is, it does not have blood clotting property.
Applications:
- Skin cutting, replace scalpel
- Remove moles, naevi, warts, lumps
- Skin resurfacing, tighten skin, remove wrinkles, improve acne scar
Non-Ablative Lasers
- Pigment Lasers
- Pulsed Dye Laser (dye laser, 510nm)
- Ruby Laser (solid-state laser, 694nm)
- Alexandrite Laser (solid-state laser, 755nm)
- Nd-YAG Laser (solid-state laser, 532nm, 1064nm)
- Vascular Lasers
- Argon Laser (gas laser, 488nm, 514nm)
- KTP Laser (solid-state laser, 532nm)
- Pulsed Dye Laser (dye laser, 577nm)
- Nd-YAG Laser (solid-state laser, 1064nm)
- Skin Tightening Lasers
- Conventional
*** Diode Laser (solid-state laser, 900nm, 980nm)
*** Nd-YAG Laser (solid-state laser, 1064nm, 1320nm, 1440nm)
*** Infrared Laser (1100 – 1800nm)
*** Erbium-Glass Laser (solid-state laser, 1540 nm)
- Fractional
*** Fiber Laser (1550nm)
*** Infrared Laser (850 – 1350nm, 1540nm)
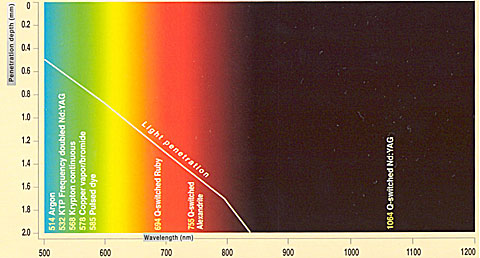
It looks very confusing indeed. As is said before, no one can know them all, even the experienced physicians. It is more important that the doctor knows his/her machines well, both in the effectiveness and limitations.
The pigment lasers have a short-pulsed (Q-switched), or long-pulsed mode, each has different indications. The targeted chromophore is melanin, or any dark-coloured pigment.
Main applications:
- Remove pigmented spots, such as freckles, café-au-lait spots, melasma
- Remove tattoo pigment
- Hair removal
The targeted chromophores of vascular lasers are oxyhaemoglobin, and cells of blood vessels.
Main applications:
-
Remove telangiectasia (red & blue lines)
- Remove birthmarks such as port wine stains, strawberry naevi
The skin tightening lasers are mainly lasers with mid-infrared wavelengths, and they target the collagen, and water content in the dermal matrix. The heat generated induces a partial injury, with subsequent dermal healing response and skin contraction. Normally some forms of cold protection is delivered at the same time, therefore no notable injury is done to the epidermis on top.
All lasers can do potential damages to the eyes and it is a must, for both doctors and patients, to wear protective eye-wears during the treatments.

We shall come across some of these lasers again in more details when we discuss the laser treatments.
Laser Skin Tightening
One of the signs of aging is sagging skin around the face and neck. While the sagging is in its early mild to moderate stage, laser skin tightening can help you to achieve smoother and tighter skin without undergoing surgical face lift, which is considerably more expensive and traumatic.
This is achieved by using non-ablative lasers, which do not remove any layers of skin from the surface. Because the epidermis is intact, there is no prolonged downtime, or the associated risks of complications from healing. It can be performed almost anywhere on the body: face, neck, abdomen, arms, legs, and buttocks.
These lasers are mainly in the near or mid infrared range, at 1064nm, 1320nm and 1450nm. They penetrate deep into the dermis, and are absorbed primarily by water content. This heats up the dermis and causes a controlled damage to the other contents, with subsequent regeneration and remodeling of new collagen and tissue, and skin tightening. This thermal damage is limited to the dermis by cooling the epidermis during the treatment
They have been demonstrated to induce new collagen formation in the papillary dermis, tighten skin, and improve skin texture and tone. Although the improvement typically seen is relatively modest comparing to laser skin resurfacing, it is compensated by the minimal risk and downtime. If you have severely sun-damaged skin and skin laxity, you would benefit more from more aggressive treatment such as fractional CO2 laser resurfacing above, but bear in mind that you would have a longer downtime too.
Because of the deeper penetration and heating effect on skin, they tend to cause a fair amount of pain during treatment, and it is necessary to apply local anaesthetic cream for an hour before treatment.
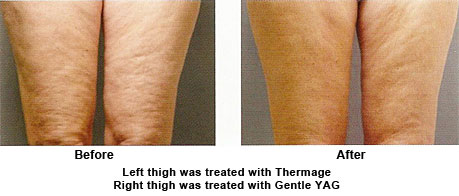
Further skin tightening occurs over the next few months after treatment, but optimal results usually require 4 - 6 treatments at a month apart. The exact treatment protocols, such as the parameters, number of treatments needed, and the interval between treatments, vary among the many different lasers in this category. The long pulsed Nd:YAG lasers provide particular benefits. One of the better- known and researched lasers is Gentle YAG laser, which is a long pulsed Nd-YAG laser with a wavelength of 1064nm.
Laser Skin Resurfacing
Laser skin resurfacing usually refers to the skin resurfacing done by ablative lasers, although confusingly, some non-ablative skin tightening lasers makers also call their treatments as “resurfacing”, despite no skin surface is removed in the process.
During the process, the laser vaporises thin layers of skin, leaving a denuded, raw surface. Then the skin will heal, providing:
- a newly regenerated epidermis, which is smoother, with wrinkles, scars and other facial imperfections becoming less noticeable, and
- re-modeling of new collagen in the dermis, and skin contraction
Types of Lasers Used
There are only two types of lasers used for (ablative) skin resurfacing in aesthetic medicine. They are CO2 laser and Erbium-YAG laser.
CO2 laser is the first, and has been the gold standard in skin re-surfacing for many years as it achieves unparallel smoothness and reduction of wrinkles that no other modality can match. It is capable of more dramatic corrections by removing layers of skin down to a deeper level, but with a longer downtime. Because it contracts skin immediately with blood clotting ability, bleeding is much less of a problem.
Erbium-YAG laser is relatively superficial (although it can go deep too), and was developed to minimise the risk of burning the surrounding tissues. It causes less post-operative side effects such as swelling, bruising and redness caused by inflammation, therefore it has a shorter downtime. This laser works best for small areas, minor or superficial wrinkles.
They can be applied to single areas or the entire face. The conventional method will use the laser to cover 100% of the area being treated. This method means a large denuded area, with rather long recovery time, typically about 3 - 4 weeks for the full face with the CO2 laser, which is really not acceptable to many people. General anesthesia may be needed when the entire face is treated. This also has a higher chance of leaving marks, or uneven pigmentation on the skin, particularly for people with darker skin types (post-inflammatory hyper-pigmentation). Because of these, this type of skin resurfacing has not been very popular among either doctors or patients.
Now the new fractional method has made a revolution, and has hit the market with great anticipation and hope. The laser will only deliver thousands of small laser beams to create microscopic wounds, which will heal up in a matter of 1 - 2 days, and scabs coming off in 4 - 7 days. The result is close to the conventional treatment, while avoiding the long downtime and potential side effects.
Fractional CO2 Laser
It can improve your skin tone, texture; reduce scars; and tighten your skin in a single treatment.
The result is close to the gold standard achieved by conventional CO2 laser resurfacing, yet avoiding the long downtime and potential risks from treatment.
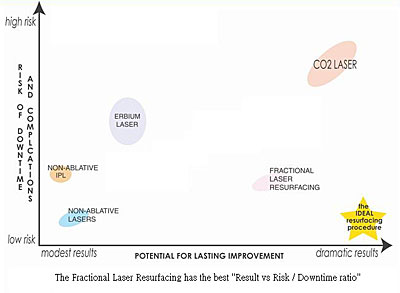
How Does It Work?
The CO2 laser beam is delivered by a high speed scanner, and thousands of microscopic holes 0.1 - 0.12mm are punched into the skin right next to each other in minutes, immediately eliminating discolourations at the surface and causing volumetric skin contraction. In a week or so when these microscopic wounds heal up, the skin is tightened further. It also stimulates more continual collagen remodeling to follow over the following months.
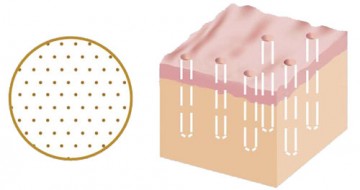

The higher the energy, the deeper it penetrates into the skin. The higher the density of the laser beams, the larger amount of skin tissue is removed.

By carefully choosing the amount of skin surface treated and the depth of penetration, the doctor can tailor treatment to the indication and patient’s tolerance of downtime.
What Are The Advantages?
- Only a small portion of the skin’s surface is treated, making the healing process much quicker with relatively short downtime, typically 4 - 7 days.
- Simply outperforms any non-CO2 based laser and device for skin rejuvenation, with results that are close to traditional CO2 laser resurfacing.
- Minimal discomfort as only topical anesthesia is needed for most individuals.
- Safe and effective for virtually all skin areas including face, eyelids, neck, chest, back, arms and hands.
- Cosmetic appearance continues to improve with stimulation of collagen production up to 6 months after procedure.
The Procedure Itself
A topical anesthetic cream will be applied for about an hour before the procedure. There is some pain associated with it but usually it is well tolerated.
The procedure takes about 10 minutes for the face. It is then followed by a cooling-off treatment with a special cooling machine, which helps to sooth the skin and reduce the redness much faster. For cases treated with higher energy, a treatment with infrared light will further shorten the healing process.
With a gentle washing and plenty of moisturiser, the tiny scabs will begin to flake off in 2 - 3 days, and last for about 5 - 7 days. You can start wearing make-up as early as day 2 or 3, as long as the wounds are dry. Pinkness should be gone in about a week.
What Are The Benefits?
It has a dramatic effect on the skin:
- Improves skin tone, glow and texture
- Reduces fine lines and wrinkles
- Softens deeper frown lines
- Tightens loose eyelids skin
- Tightens skin around the neck and jowls
- Tightens loose skin in the tummy and reduces white lines from pregnancy
- Softens scars, especially acne scars
Treatment Examples
The following examples show results after just one single treatment:
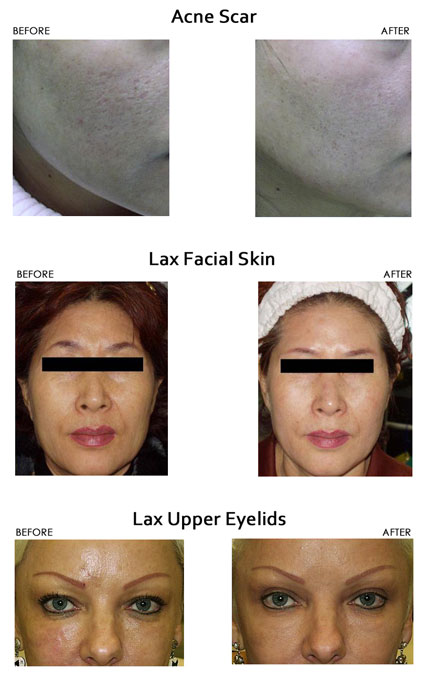
The results are long-term and, with proper sun protection, can persist for many years. Most effects of treatment become visible very quickly, whereas others, such as new collagen formation, build up gradually and become more evident over time. Therefore, most people look even better 3 - 5 months after the procedure.
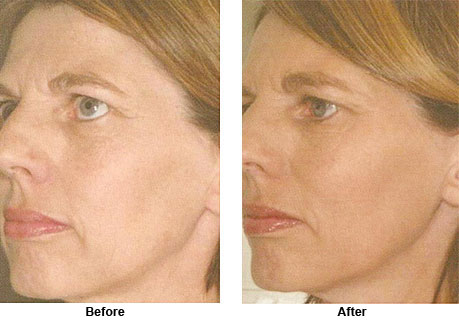
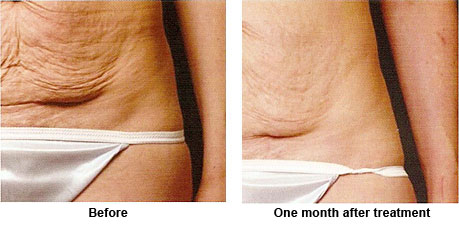
Gentle YAG Laser
The GentleYAG laser is a long pulsed Nd-YAG laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm, which is in the mid infrared range. Evidences suggest that lasers in this range may be the best choice for safe non-ablative laser skin tightening on a wide range of skin types, including tanned skin.
It safely and effectively treats a wide variety of cosmetic skin problems. Apart from skin tightening and treating wrinkles, it offers treatment capabilities in hair reduction, leg veins, and facial veins.
How Does It Work?
It can penetrate deep into the dermis, heat up the dermal contents, and stimulate more collagen remodeling. New collagen growth will continue for four to six months post treatment.
Its wavelength is weakly attracted to melanin, and therefore there is reduced risk of heating up and burning the epidermis. What is more is that, it has a patented Dynamic Cooling Device (DCD), where a cold cryogen is sprayed onto the skin, cooling the upper layers just before the laser fires. This further protects the epidermis from thermal damage, and provides patients with maximum comfort.
It has a large treatment spot size up to 18mm, which means the treatment is fast, with fewer laser pulses.
Treatment Examples
Treatment Procedures
Like any other skin tightening lasers, there is a fair amount of pain during treatment, which is usually described as snaps by a rubber band. This can be minimised by application of a topical local anaesthetic cream for an hour before the treatment.
Shot after shot, the laser is applied to the whole treatment area. Usually a second or even a third pass is done to maximise the dermal response.
After the treatment, there is a warm to hot feeling, with some associated redness. These will gradually disappear in a couple of hours, and there is no trace of treatment. As a result, the downtime is absolutely minimal and you can return to normal activities immediately.
Some patients have reported that they can see results in just a few days after treatment; however, the optimum results occur anywhere from 4 - 6 weeks after the treatment. A second treatment may be done approximately 6 weeks apart. The number of treatment depends on the severity of skin laxity, and usually falls between 4 - 6 treatments.
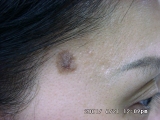
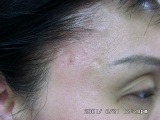
Moles Removal
Many people call those pigmented growth on the skin as moles. Fair skin individuals, tend to have more number of moles on their body, partly because they are more liable to sun damage. Most of the time they are benign moles and can be removed for cosmetic reason. Occasionally they are, or can turn cancers. When there is uncertainty regarding the nature, it should not be removed with a laser, but rather it should be cut out whole and sent for laboratory examination.
Medically, moles are called naevus (plural: naevi). There are 4 types: junctional, intra-dermal, compound, and blue naevi
- Junctional: The naevus cells are in the epidermal-dermal junction. They appear black and are flat.
- Intradermal: The naevus cells descend into the deep dermis, and the naevus loses the black colour gradually while becoming more and more raised. With time it appears as a large skin-coloured dome-shaped lump.
- Compound: Somewhat in the middle between the above two. The are slightly raised with variable degree of black pigment.
- Blue naevus: it is blue in colour as the melanocytes are very deep in the dermis.
These benign moles were once traditionally cut out by the physicians. This required sutures and there would be a scar, which can be cosmetically very unacceptable, particularly when on the face. This method should really not be used for cosmetic improvement.
You can now have your moles removed with 2 different lasers : a pigment laser and a CO2 laser, with far more superior cosmetic result.
Pigment Laser
A Q-switched ND-YAG 532nm or 1064 nm is used. The laser is absorbed by the melanin in the naevus, and the heat shatters the melanin into smaller fragments, which are removed internally by cells called macrophages.
As the pigment load is much higher than, for example freckles, this usually requires multiple sessions, and the black pigment is removed only gradually, with a lighter appearance after each treatment.
This method is used mainly on junctional naevi, which are flat, and is recommended if you have many of these. When you have only a few, say less than 3 - 4, with small sizes, it is much more efficient to vaporise them with a CO2 laser in one single session, and let the small wounds heal on their own.
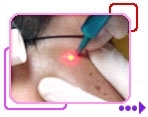
CO2 Laser
Since the compound and intra-dermal naevi are elevated, in order to achieve good cosmetic results, they need to be re-surfaced to the same level as surrounding skin, in addition to removing the black pigment.
As the CO2 laser is absorbed by the water content and heat up the tissue, it burns and vaporises the skin, layer by layer. Therefore it can scrap the lump gradually down to a flat level. The black pigment is vaporised altogether at the same time.
Sometimes all the black pigment is within the elevated part, and no deeper than the skin level, and the wound is very shallow. Usually it is not the case, and we need to dig deeper into the skin, leaving a wound like a small hole. If the pigment is too deep, then we need to use the pigment laser on this wound too after the CO2 laser.
The wound, either flat or as a small hole, will heal up after a few days, usually about a week. There may be a light reddish-brown mark after, but it will almost for sure fade away gradually, in 1 - 3 months, although sometimes it can take longer.
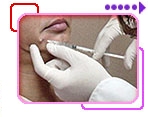
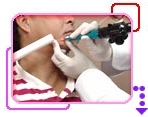
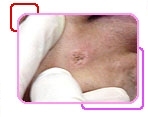
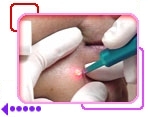
|
CO2 Laser Treatment Example 1 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
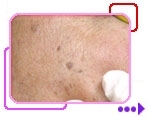
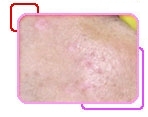
CO2 Laser Treatment Example 2 |
||
 |
 |
 |
Treatment Examples
Junctional Naevi
 |
 |
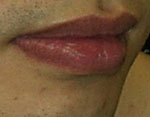 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
1 Month After
|
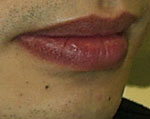
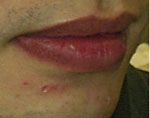
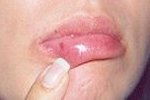
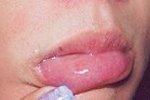
Naevus on Lips
 |
 |
|
Before
|
2 Weeks After
|
 |
 |
|
Before
|
2 Weeks After
|
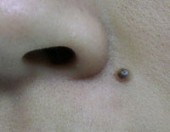
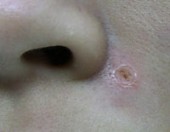
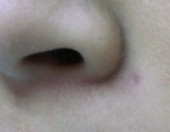
Compound Naevi
 |
 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
 |
 |
|
1 Week After
|
1 Month After
|
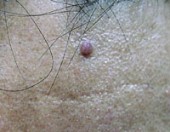 |
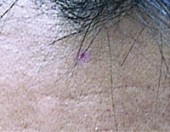
 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
 |
 |
|
1 Week After
|
1 Month After
|
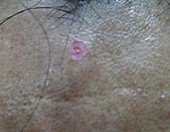
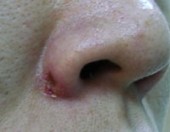
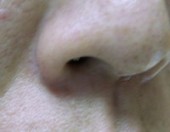
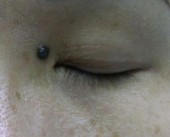
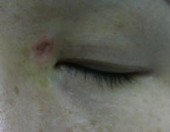
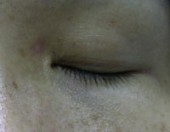
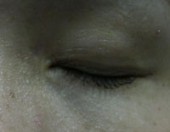
Intra-dermal Naevi
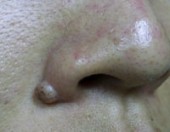 |
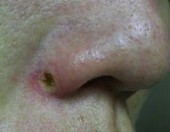 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
 |
 |
|
1 Week After
|
1 Month After
|
 |
 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
 |
 |
|
1 Week After
|
1 Month After
|
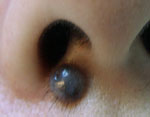
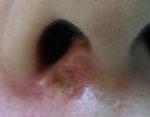
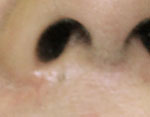
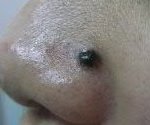
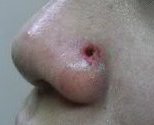
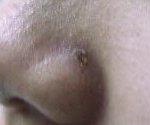
Blue Naevi
 |
 |
 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
1 Week After
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
2 Weeks After
|
Facial Warts Removal
All warts are infection of the skin surface by the human papilloma viruses. The commonly encountered warts on face are:
- Comman warts
- Plane warts
- Seborrhoeic warts
Common Warts
They are round lumps with an uneven surface like that of a cauliflower, although sometimes they can have a smooth surface. They are very common on the hands and fingers, and frequently spread to other parts like the face by touching and scratching. Cases have been seen with warts on any parts of the face, including the nostrils.
Plane Warts
They appear as fleshed-coloured or pigmented, very slightly raised, well-defined and flat-topped lumps. They are particularly common on the face and hands. When they are small they are not very noticeable, but with time they will spread and become much larger, and numerous of these seem to appear suddenly and can be cosmetically alarming.
Seborrhoeic Warts
They are actually not warts and should be called seborrhoeic keratosis. They are caused by excessive growth of the top layer of epidermis and are related to skin aging and sun exposure. They are usually found in people over 30 years old, and tends to become more common and more numerous with age. They can be solitary or in clusters and appear light tan to black colour, with sizes range from a few mm to a few cm. It is unsightly when there are numerous of them appearing on the face. Removal is sometimes recommended not just for cosmetic reason, especially if they get irritated and bleed easily.
All of the above are easily removed by scrapping off with the based cauterized afterwards, or the whole thing can be burnt off by a CO2 laser. These are more effective than freezing treatments using liquid nitrogen. The wounds will heal up after about 1 week and there should be no scars.
Treatment Examples
Warts
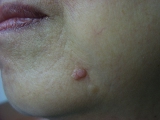 |
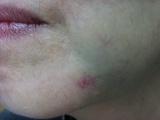 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
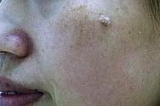 |
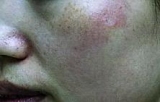 |
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
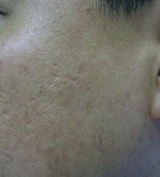
Plane Warts
 |
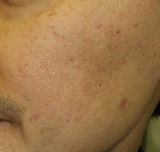 |
|
Before
|
1 month After
|
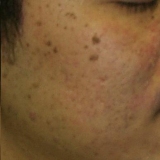 |
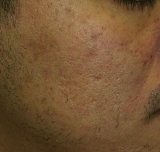 |
|
Before
|
1 month After
|
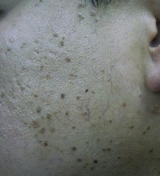 |
 |
|
Before
|
3 months After
|
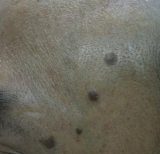
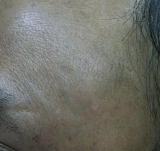
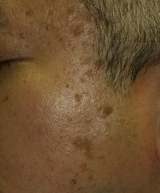
Seborrhoeic Keratosis
|
|
|
|
Before
|
Immediate After
|
 |
 |
|
Before
|
1 month After
|
 |
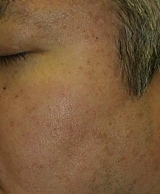 |
|
Before
|
3 months After
|
Pigment Spots Removal
The commonest acquired pigmented spots encountered in the aesthetic consultations are freckles, solar lentigines, and melasma. Café-au-lait spots become more apparent in early childhood.
All these pigmented problems can be aggravated by sun exposure and so it is important to apply sun protection while seeking treatment to remove them. As mentioned before, melasma is notoriously difficulty to get treated by laser and some doctors would avoid to treat it, because of the potential complications.
What Lasers Are Used?
The lasers used in this aspect must have wavelengths that are well absorbed by the melanin pigment. The commonly used include 510nm, 532nm, 755nm and 1064nm. They are all excellent in removing freckles and solar lentigines.
The 510nm is a pulsed dye laser, while 532nm, 1064nm and 755nm are solid-state lasers, and are opearated in two available but separate modes: the Q-switched (QS) mode and the long-pulsed (LP) mode.
Q-switched (QS) mode
It allows the laser energy to go through the filter in an ultra-short time (nano second). The result is a more explosive nature, which can thermally and mechanically shatter the pigment into very small fragments, and removed by our own system.
However, it has a small spot size of 3 - 4 mm, and so can target only individual spots, one at a time. The result is, there may be uneven colour between treated spots and the surrounding non-treated skin. It also causes a lot of redness and swelling after treatment, which may take up to a week to resolve. Because of these factors, you cannot have the whole face treated with this laser.
All 3 wavelengths have a QS mode: QS 532nm, QS 755nm, Qs 1064nm.
Long-pulsed (LP) mode
It is a newer version. The laser energy is delivered through a longer period (milli second), and the pigment is burnt by this prolonged heating.
It has a much larger spot size, and can be used to cover a large area in minutes. It is also more gentle in that it causes a lot less redness and swelling, typically 1/3 of that caused by QS lasers, and is apparent only on the pigmented spots. The downtime is a little shorter, by 1 –2 days. Because of these, it is very easy to use on the whole face, taking pigmented spots off, as well as lightening the skin colour for the rest of the face.
Only LP 755nm is popularly used for this. LP 1064nm is relatively less absorbed by melanin and is mainly used for laser hair removal.
Treatment examples:
QS 755nm
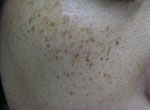 |
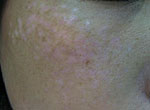 |
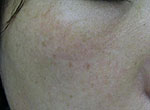 |
Note the temporary paler colour in the treated areas 1 week later, compared to surrounding skin. Last picture after 2 months.
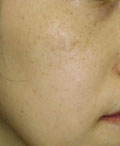 |
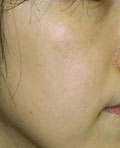 |
LP 755nm
Mild Freckles
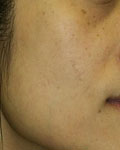 |
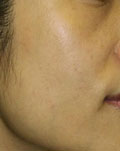 |
Moderate Freckles & Solar Lentigines
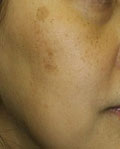 |
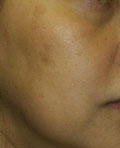 |
Mixed Pigmented Spots
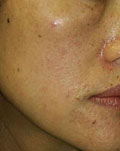 |
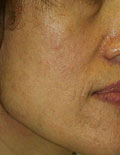 |
Chest
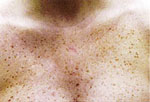 |
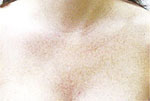 |
Back
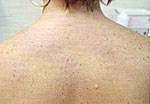 |
 |
Hair Removal
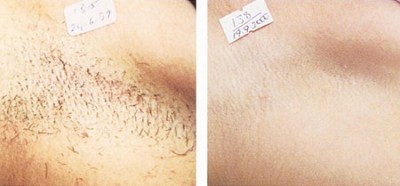
A lot of people are troubled by excessive hair growth on their body. Different methods have been tried, such as shaving, waxing, and electrolysis, but none of these is as effective as laser hair removal, which leaves skin looking smooth and silkier.
How Does It Work?
Lasers are used to target the melanin pigment at the root of the hair follicles. The intense heat generated destroys the hair follicles instantly, and slows hair regrowth. Common treatment sites include legs, armpits, upper lip, chins and bikini lines. However, it is possible to treat unwanted hair in almost any area of the body.
As it is the root that is being targeted, excess hair on the surface will absorb the laser, preventing the laser from reaching the bottom, and reduce the effectiveness. What is more, the burnt hairs will in turn burn the skin and cause problems. Therefore it is most effective if hairs are shaved short. You can shave on the day of the procedure.
We use top of the range laser models, the GentleLASE (Long-pulsed 755nm) and Gentle YAG lasers (Long-pulsed 1064nm). They have the patented Dynamic Cooling Device, which sprays a short purge of cold cryogen just before the laser is emitted, thus offers extra protection from burning the epidermis, and adds maximum comfort. This is superior to the cold contacts of some other models.
Both are extremely effective in the hair removal. The GentleLASE is almost the gold standard these days, and can be used on skin types I to IV. The GentleYAG has less attraction to black melanin and is more suitable for people with darker skin types, from IV to VI, as it will have a much lower chance of causing skin burn.
The hair colour will affect the success of hair removal as well. Brown to black hair can be removed very successfully, while laser does not work for white, blonde, light brown or light red hair.
Treatment Procedures
The skin is checked for excessively long hair for reason above, and extra shaving may be done at the clinic for you. You need to wear goggles to prevent accidental exposure of your eyes to laser light. You would feel the cold spray and then a quick snap, which is quite minimal and well tolerated. Local anaesthetic cream prior to treatments is not necessary for these machines.
As both the GentleLASE and Gentle YAG lasers have large spot sizes up to 18mm, they are very fast in conducting the treatments, typically only a few minutes for the underarms, and around 20 minutes for the whole back. There may be an odour of singed hair, which is normal. You may notice some redness and swelling, and extra cold compress may be applied. This only lasts for the first 1 - 2 hours. You can return to work on the same day. However, you should protect the treated areas from strong sunlight for the first few days.
Treatment Course
It takes several treatments to provide an extended "hair-free" period, which can vary from several months to many years. Each treatment is separated by 4 - 6 weeks. The number of treatments required is usually between 2 - 6, as it varies with individuals, and the personal expectation. Someone who wants totally hair free for a long time would need more, while someone who is happy enough to see thick coarse hair turning into normal fine hair would require less, may be just 2. Thereafter, only one periodic maintenance treatment is required.
Treatment Examples
| Underarms |
|
| Bikini Lines | 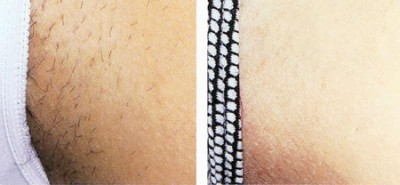 |
| Facial Hair | 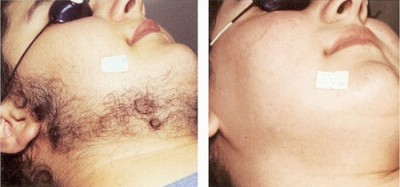 |
| Back | 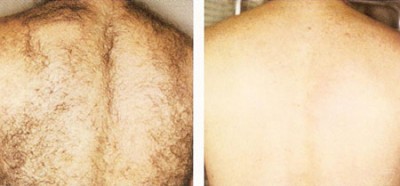 |